
We are living in the age of technology where everything is “e-ed”. That means e-bills, e-payment, e-storage, e-music, e-booking, and so on with all e-categories. We have made tremendous progress in Science and Technology and we have produced many electronic or electrical devices to bring ease to our life.
Almost everything on a click, we get to solve our day-to-day necessities needs. But, like any other material thing, such devices also wear down, misfunction. Sometimes we simply get better options in the market leaving room for electronic waste. That means our waste are also becoming “e-ed”.Yes, they become waste once we discard them. The latest trends are becoming the status symbol for people and hence the older devices are getting out of use.
A friend of mine recently opened his memory bag, ie. the bag in which he kept his college memories, almost after 5 years. The bag had along with other memories - the first mobile he used during the college days, a mobile charger, an earphone, 2 pen drives that he used during lab assignments, a small micro-controller from his project assignment, and a few CDs. Do you think he is going to use them now? Do you think they are functioning well now? No way! He is not going to use it. And he doesn’t know what to do with it now.
We still do not know about e-waste and what all it includes. We carry it unknowingly. So let’s first understand what is e-waste and what it contains. So on broader term e-waste are the electrical and electronic items that are discarded after use or generated through manufacturing processes. So they can be any household item or any industrial item or products that came to the end-of-lifecycle phase for a particular kind of use. One of the primary reasons behind increasing e-waste is rapid technology growth and trending consumer choices with increasing ease which automatically generates a willingness to buy new products while old is still functioning well.
Based on its composition and components such as metals, glass, plastic, etc. e-waste can be categorized into multiple categories. Let’s understand in the below table what goes into e-waste (Based on European Union Categorization which is widely accepted).
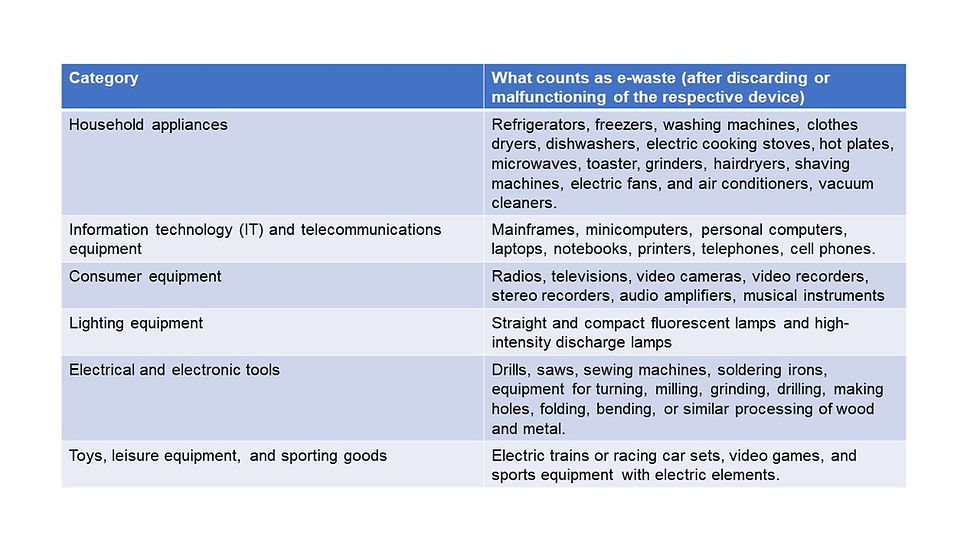
Apart from the above list from our daily usage, medical devices, automatic dispensers eg. coffee vending machine, monitoring and controlling instruments eg. smoke detectors are also part of e-waste categories when out of use or damaged beyond repair.
Iron and Steel are the major constitutes of e-waste followed by plastic and then non-ferrous metals (Aluminum, Copper, Gold, Lead, Silver, etc.). As we see in the below image, most of the e-devices and hence the e-waste contain various hazardous and non-hazardous elements.

The presence of elements like Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, Selenium in e-waste beyond limit can stand harmful for the environment and health of living beings as they create serious pollution upon disposal. If e-waste is not recycled or disposed properly, it ends in the landfill and remains untreated forever. They automatically start creating an adverse effect on human or animal health, soil, water bodies, and food chains.
The seriousness comes into the picture from these numbers.
The worldwide disposal of e-waste is around 50 million tonnes per year which is greater than the weight of all the commercials airlines ever made says a UN University study report. And India is one of the top five countries in the e-waste generation. More to that is India generates more e-waste than it has the capacity to process it.
So, it’s high time to act about e-waste before it grabs us like plastic waste. Let’s be smart not only in using smart e-devices but also in dealing smartly with e-waste. Stay tuned to the next wlog where we see how we can wisely deal with e-devices and e-waste.
How did you like our Wlog. Share your feedback at connect@inwaster.com

Comments